Introduction
In this lesson, you will review how to find the x- and y-intercepts of a line.
This video illustrates the lesson material below. Watching the video is optional.
X- and Y-Intercepts
Intercepts are an important part of graphs. They indicate a lot about data. For example, y-intercepts often give a starting amount. Here are some vocabulary words to help you with this lesson:
- x-intercept: where the graph crosses the x-axis, and where \(y = 0\)
- y-intercept: where the graph crosses the y-axis, and where \(x = 0\)
The x-intercept is anywhere that the line crosses the x-axis. The x-axis is also known as the horizontal axis. The y-intercept is anywhere that the line crosses the y-axis.

Figure 1
At the y-intercept point, \(x=0\). Similarly, at the point at which the line crosses the x-axis, \(y=0\). At the point where the line crosses the x-axis, y will always be 0. The value of x will change depending on the line, but any time the line crosses the x-axis, \(y=0\).
Any time the line crosses the y-axis, x has to be 0. The value of y may be different, but the y-axis will be where it crosses.
When you know this information, you still need to estimate the value of x for the x-intercept and the value of y for the y-intercept.
Example 1
Estimate the x-intercept and y-intercept of the line in Figure 2.

Figure 2
If you look at the x-intercept, you can estimate it at 1.5. The estimated x-intercept is written as: \((1.5, 0)\).
The y-intercept is approximately at 3. The estimated y-intercept is written as \((0, 3)\).
Things to Remember
- At the x-intercept point, \(y=0\).
- At the y-intercept point, \(x=0\).
Practice Problems
Use the following graph to answer questions 1 through 6.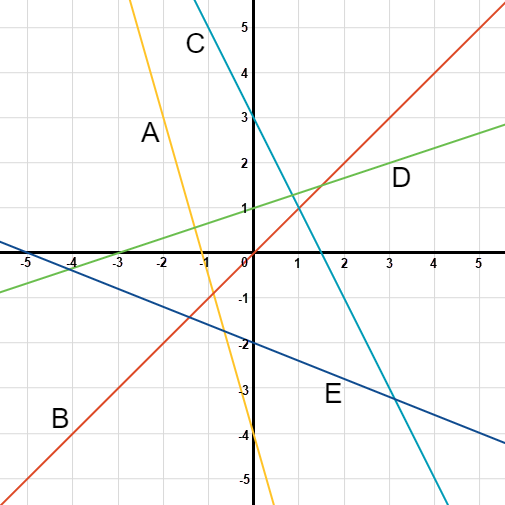
- What is the y-intercept of line A? (
- What is the x-intercept of line B? (
- What is the y-intercept of line B? (
- What are the x-intercept and y-intercept of line C? (
- What are the x-intercept and y-intercept of line D? (
- What are the x-intercept and y-intercept of line E? (

